Site24x7's Google Cloud monitoring onboarding method: Service Account Impersonation
This help document will explain the step-by-step process of Google Cloud monitoring with authentication via the Service Account Impersonation method.
Prerequisites
Authenticate via the Service Account Impersonation method
Step 1: Creating a Service Account
- Log in to the Google Cloud console.
- Go to IAM & Admin > Service Accounts.
- Create a Service Account with your required inputs, like the display name.
- Assign the necessary permissions to this Service Account.
Step 2: Assigning Site24×7's principal email address to the Service Account
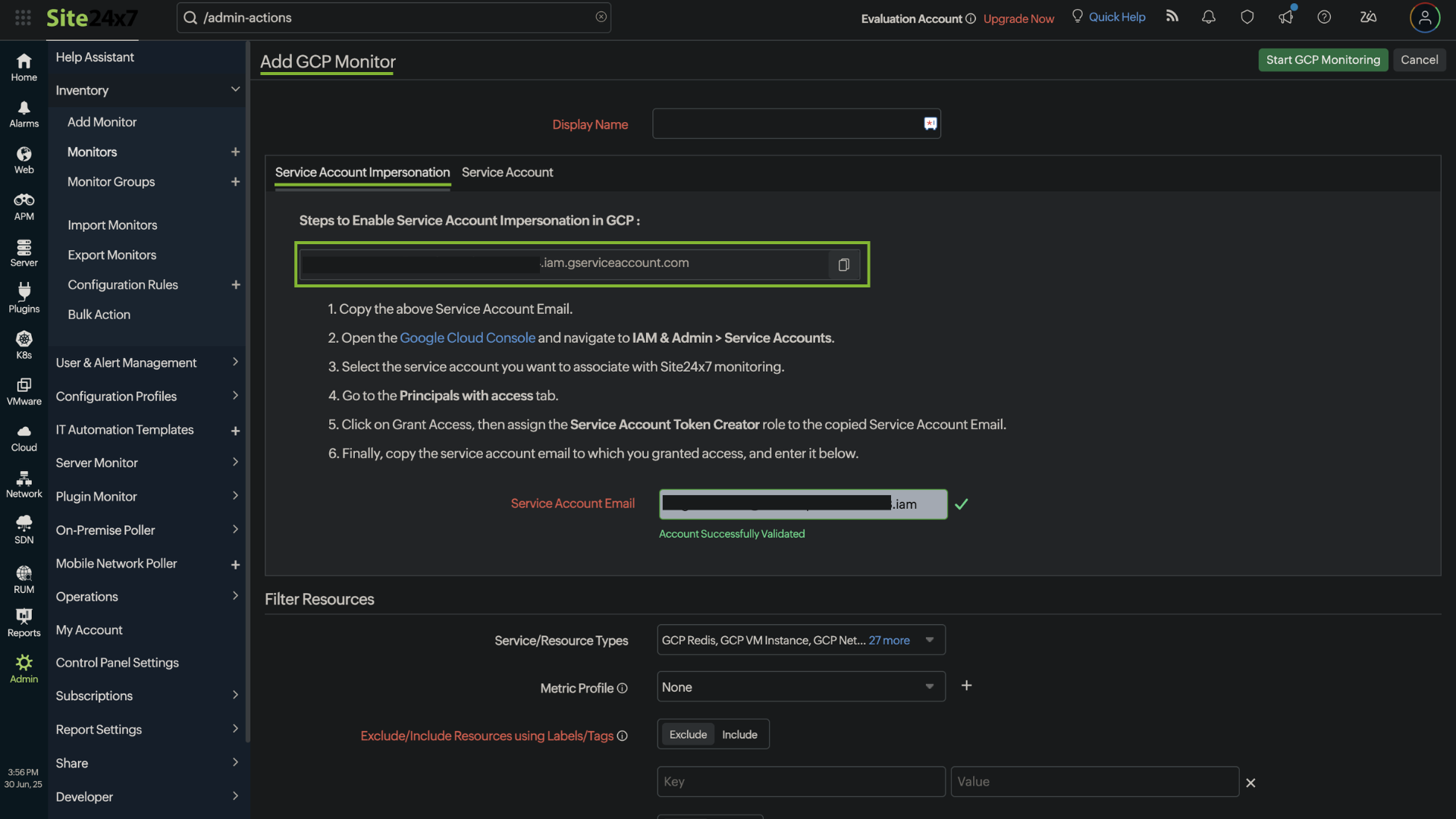
- Open the Site24x7 web client and go to Cloud > GCP > Add Monitor > Service Account Impersonation.
- Copy the Site24x7 service principal shown on the Site24x7 Add GCP Monitor page.
- In the Google Cloud console, in the Service Accounts menu, find the Service Account you created in Step 1.
- Go to the Permissions tab and click Grant Access.
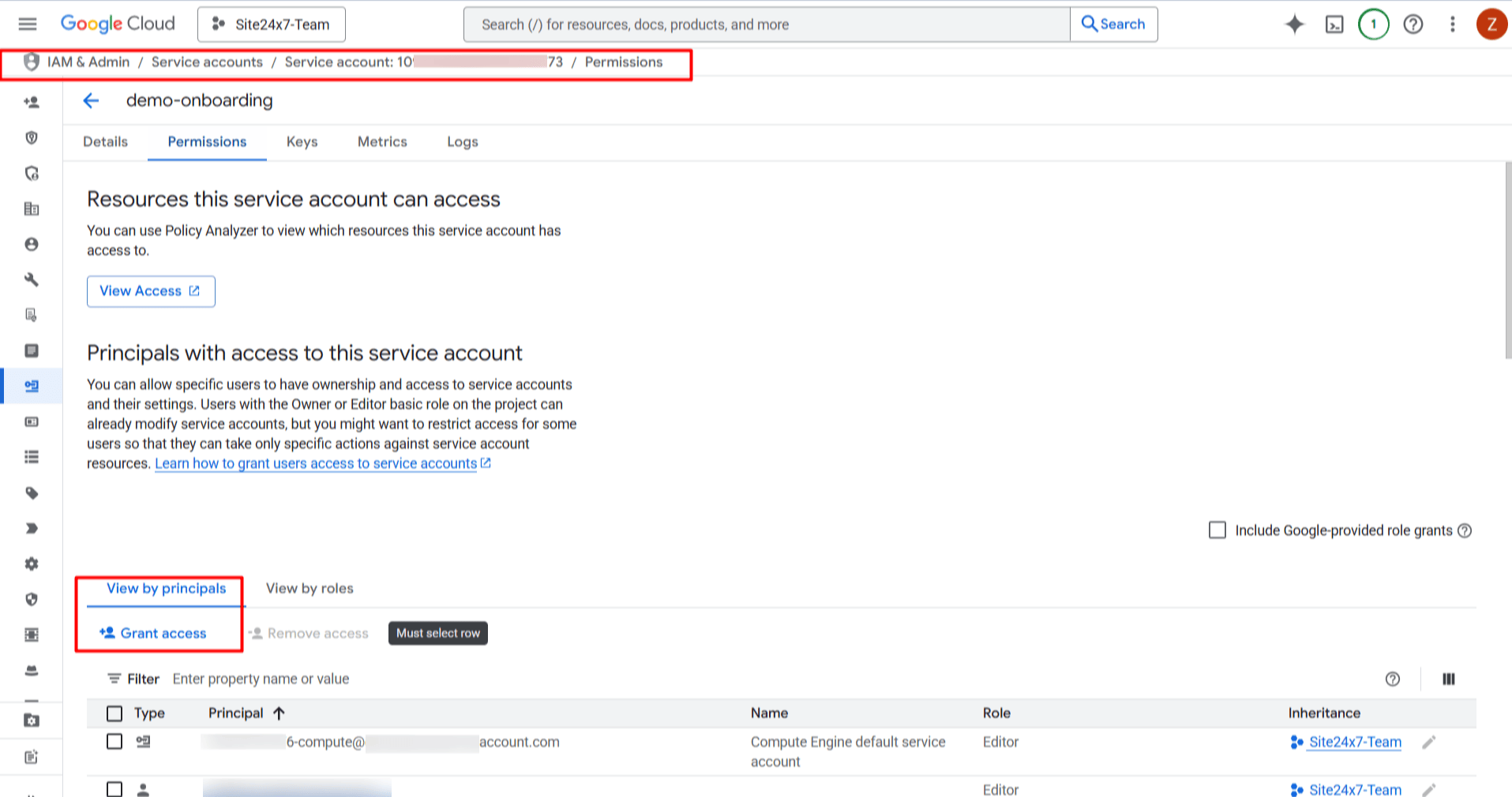
- Paste your Site24x7 principal into the New principals text box.
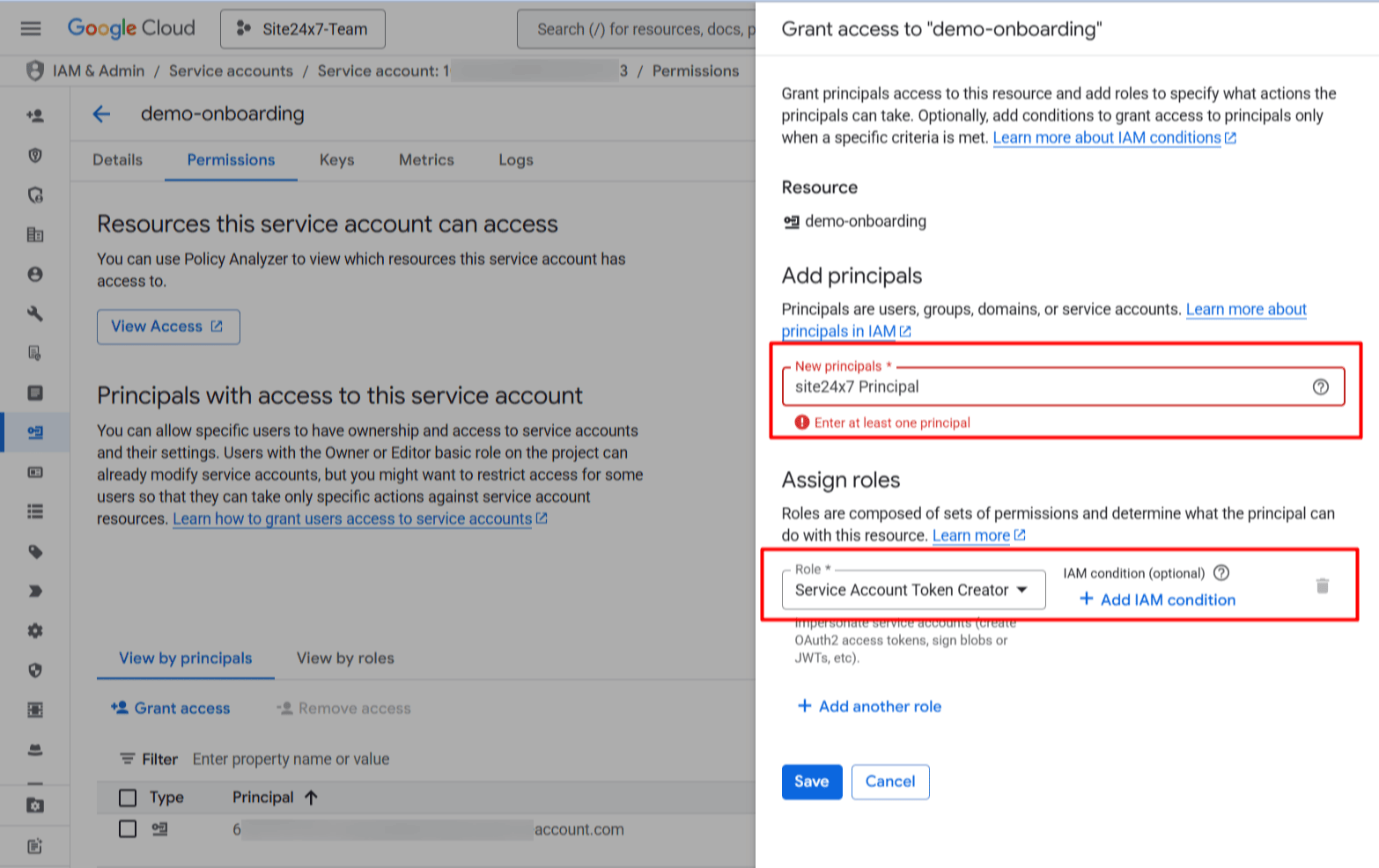
- Assign the role of Service Account Token Creator and click Save.
- Paste your Site24x7 principal into the New principals text box.
- Copy the Service Account Email.
Step 3: Entering the Service Account's email address in Site24x7 for monitoring
- Open the Site24x7 web client and go to Cloud > GCP > Add Monitor.
- On the Service Account Impersonation tab, paste the Service Account Email you copied earlier.
- Fill in the display name for easy identification of the account.
- Proceed to filter the resources based on your monitoring requirements.
- Once you've configured the settings above, click Start GCP Monitoring.
Common troubleshooting instructions
- Access errors: Ensure that the Service Account has the correct permissions and that the principal is added with the appropriate roles.
- Missing resources: Double-check your filters to ensure all the intended resources are included or excluded as desired.
Reasons for migration to the Service Account Impersonation method
Service Account keys are persistent credentials that, if exposed, can lead to unauthorized access and privilege escalation. Service Account Impersonation, on the other hand, generates short-lived credentials that are valid only for a limited duration. This reduces the risk of misuse and ensures credentials are not stored permanently.
Impersonation requires a previously authenticated identity, adding an extra layer of security. It allows administrators to manage permissions and access centrally without distributing keys.